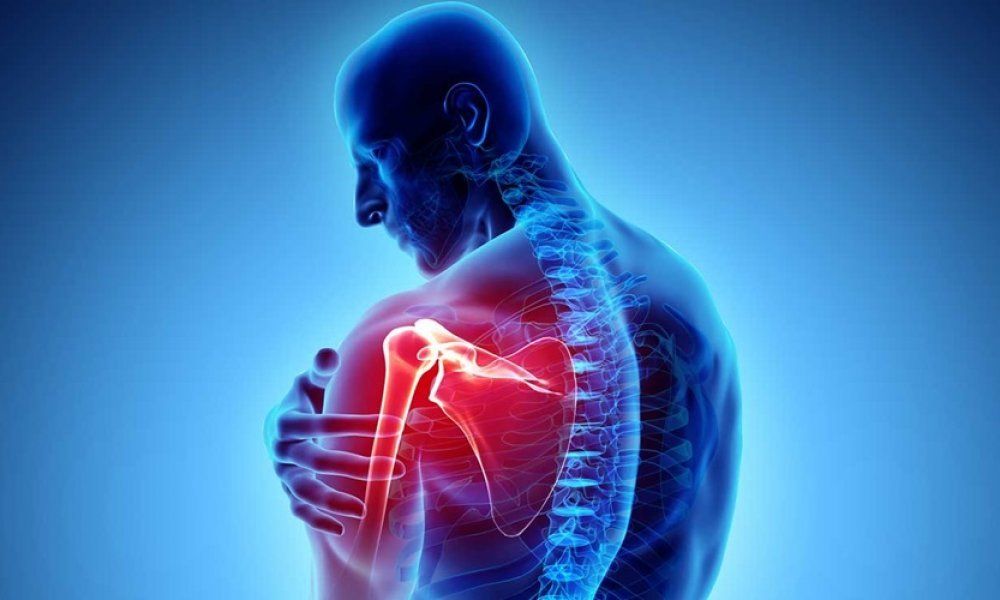
What is the Rotator Cuff?
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder keeping head of the humerus firmly within the socket of shoulder joint.
What are the 4 Muscles of the Rotator Cuff?
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Subscapularis, Teres Minor.
What is the Main Function of the Rotator Cuff?
The Rotator Cuff has the important jobs of stabilising the shoulder, elevating and rotating the arm, and ensuring the head of humerus stays securely in place in the shoulder socket.
What motion does each rotator cuff muscle do?
- Supraspinatus controls internal rotation and lifting of the arm.
- Infraspinatus allows you to externally rotate your arm in the shoulder socket.
- Teres minor is a small muscle that helps rotate your arm.
- Subscapularis controls arm abduction (holding your arm out straight, away from your body).
All four muscles work together to centralise your humerus bone in the shoulder joint, so when you lift your arm up, your arm up, your rotator cuff muscle tighten and pull the joint together, stabilising your shoulder.
What are the most common injuries of the rotator cuff?
Common injuries include tendonitis and strain, which is a partial or complete tear of the rotator cuff muscles. Tendonitis is inflammation or irritation in the tendons and cuff muscles that help move your shoulder joint.
How can you tell the difference between rotator cuff tear and tendonitis?
Both have similar symptoms like pain, swelling, and stiffness. With a tear, the arm can barely move overhead. Tendonitis tends to happen over months, even years, of overuse. Tears, however, are sharp pains that generally occur after a sports collision or accident.
What factors contribute to rotator cuff injury?
Rotator cuff injuries are most often caused by progressive wear and tear of the tendon tissue over time. It might be caused by poor posture, repetitive overhead activity or prolonged bouts of heavy lifting that can irritate or damage the tendon. The rotator cuff can also be injured in a single incident during falls or accidents.
What are the most common symptoms of a rotator cuff injury?
- Pain or swelling in the front of shoulder and side of arm
- Pain when raising and lowering arm
- Clicking or popping sound when arm is moved
- Pain that disrupts sleep
- Loss of mobility and strength in arm
How to diagnose a rotator cuff injury?
Doctors will send you for an X-Ray and MRI to confirm the injury.
Physio or Sports Therapist will perform a couple of tests to observe strength and range of motion to diagnose the injury but will also send you for an X-Ray/MRI to diagnose severity of the injury if they feel that you will need medical help with injury
What treatments can be used to help with a Rotator Cuff injury?
Most Rotator Cuffs injuries can be treated non surgically with anti-inflammatory medication, steroid injections and Sports Therapy/Massage. Anything more severe can be treated by arthroscopic surgery.
What is the best therapy for rotator cuff injury?
Physical therapy is usually one of the first treatments suggested. Exercises tailored to the specific location of your rotator cuff injury can help restore flexibility and strength to your shoulder. Physical therapy is also an important part of the recovery process after rotator cuff surgery.
How can I treat rotator cuff pain at home?
- Over-the-counter medicine. Anti-inflammatory pain relievers like aspirin ibuprofen a can help ease your shoulder ache.
- Rest. You’ll need to stop any physical activity that causes or adds to your shoulder pain.
- Ice. A cold pack can help reduce swelling and pain. Use for 15 to 20 minutes every few hours.
- Heat. Once your pain starts to go away, you can use a heating pad to lessen any stiffness in your shoulder.
- Stretching
and strengthening rehab exercises. Your therapist can give you daily exercises to do at home to get your shoulder more flexible. Doing these in a hot shower may help.
How long does it take to recover from rotator cuff injury?
Usually, an acute rotator cuff will heal in 2 to 4 weeks. But if it is a severe injury, or it is a chronic injury from wear, it may require months to improve.
If the pain is getting in the way of your daily life or you injure yourself again, your doctor might suggest:
- Steroids. A shot injected in your shoulder joint can help with the soreness.
- Physical therapy. Your trainer can guide you through exercises to help you regain strength and motion in your shoulder.
- Surgery. This is rare. Unless you’re young and had an acute, traumatic shoulder injury, surgery is a last resort for rotator cuff tears.
Why is it worth seeing Sports Therapist for rotator cuff injuries?
Most people will benefit from seeing a physiotherapist/Sports therapist or even a sports massage therapist, who can help figure what is causing the shoulder pain and work on restoring normal Range of Motion and strength. A therapist will provide modalities to control shoulder pain and advise shoulder exercises to restore full mobility of the joint. These can include ROM exercises, stabilisation exercises, isometrics and resistance band strengthening.
What rehab exercises can you do for a rotator cuff injury at home?